In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining energy levels is more crucial than ever. Whether you’re a busy professional, a student burning the midnight oil, or someone simply trying to keep up with daily demands, understanding the intricacies of how our bodies produce and utilize energy can be empowering. At the heart of this complex process are B vitamins, often referred to as the building blocks of a healthy body. These essential nutrients play a pivotal role in converting the food we eat into the energy we need to function optimally. In this article, we’ll explore the specific roles of B vitamins in energy metabolism, unraveling the science behind their importance while offering practical insights into how you can ensure your body receives the right balance. Join us on this enlightening journey to better energy management, and discover how a deeper understanding of B vitamins can enhance your well-being and vitality.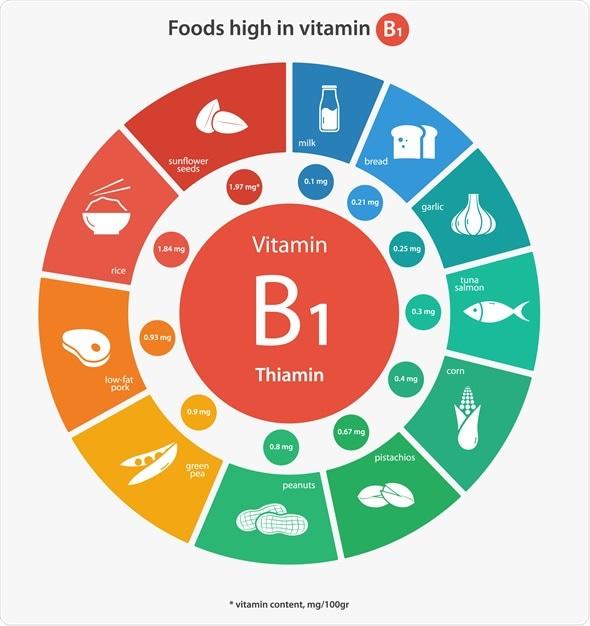
Understanding the Vital Functions of B Vitamins in Your Energy Pathways
When it comes to unlocking energy from the foods we eat, B vitamins are the unsung heroes. These essential nutrients work as coenzymes, meaning they assist enzymes in catalyzing crucial biochemical reactions. Each B vitamin plays a distinct yet complementary role in your body’s energy metabolism. For instance, Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) is crucial for converting carbohydrates into energy, while Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) and Vitamin B3 (Niacin) are integral in electron transport chains that produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Consider the following vital functions of B vitamins:
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Integral in the synthesis of coenzyme A, a key player in the Krebs cycle.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Facilitates amino acid metabolism, supporting energy production and neurotransmitter synthesis.
- Vitamin B7 (Biotin): Essential for fatty acid synthesis and breakdown, contributing to energy production.
Understanding how these vitamins contribute to energy metabolism can empower you to make informed dietary choices. Here’s a quick reference table to visualize their roles:
| B Vitamin | Primary Function | Key Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamine (B1) | Carbohydrate metabolism | Whole grains, pork |
| Riboflavin (B2) | Energy production | Dairy products, eggs |
| Niacin (B3) | ATP production | Poultry, fish |

Nurturing Your Bodys Energy Production with B Vitamins
Imagine your body as a well-oiled machine. For it to function optimally, every part must work in harmony, and this is where B vitamins come into play. These essential nutrients act as catalysts in energy production, ensuring that the food you consume is efficiently converted into fuel. Let’s delve into how you can support your body’s energy production by focusing on these vital vitamins.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): Plays a crucial role in converting carbohydrates into energy.
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Aids in breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and is vital for energy release.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Supports the function of enzymes involved in energy production.
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Essential for the synthesis of coenzyme A, a participant in the Krebs cycle.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Assists in amino acid metabolism and the creation of neurotransmitters.
- Vitamin B7 (Biotin): Vital for the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
- Vitamin B9 (Folate): Supports DNA synthesis and repair, crucial for cell growth and energy production.
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Essential for nerve function and the formation of red blood cells.
Consider incorporating a diverse range of foods into your diet to ensure you’re getting a balanced intake of these B vitamins. Here’s a quick guide:
| Vitamin | Food Sources |
|---|---|
| B1 (Thiamine) | Whole grains, pork, fish |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | Eggs, almonds, spinach |
| B3 (Niacin) | Chicken, tuna, lentils |
| B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Avocados, yogurt, sunflower seeds |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Bananas, chickpeas, potatoes |
| B7 (Biotin) | Egg yolks, nuts, soybeans |
| B9 (Folate) | Leafy greens, oranges, beans |
| B12 (Cobalamin) | Fish, meat, dairy products |

Practical Tips for Incorporating B Vitamin-Rich Foods into Your Diet
- Start Your Day Right: Kick off your morning with a bowl of fortified cereal, a perfect blend of taste and nutrition. Look for options that are enriched with B vitamins like B12 and folic acid. Pair it with a glass of orange juice or a slice of whole-grain toast to enhance absorption.
- Snack Smart: Opt for nutrient-rich snacks like almonds and sunflower seeds. These are not only rich in B vitamins such as B1 and B6 but also provide healthy fats and protein. Keep a small pack in your bag for a quick energy boost during the day.
- Protein-Packed Meals: Incorporate lean meats like chicken and turkey into your meals. These are excellent sources of B3 and B6, crucial for energy production. For a plant-based option, consider adding lentils or chickpeas to your salads and stews.
| B Vitamin | Food Source | Serving Suggestion |
|---|---|---|
| B1 (Thiamine) | Whole Grains | Swap white rice for brown rice |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Bananas | Add to smoothies or oatmeal |
| B12 (Cobalamin) | Eggs | Include in breakfast omelets |
Plan Ahead: When meal prepping, think about incorporating B vitamin-rich foods throughout the week. Create a diverse menu that includes various food groups to ensure a balanced intake. For instance, a quinoa salad with spinach and nuts not only covers several B vitamins but also offers a delightful taste.
Empowering Your Daily Energy Levels with Targeted B Vitamin Supplements
Imagine your body as a high-performance engine, constantly requiring the right fuel to function optimally. This is where the B vitamins step in, acting as essential co-factors in energy metabolism. They help convert the food you eat into usable energy, supporting a range of physiological processes that keep you active and alert.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), for instance, plays a crucial role in the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, making it indispensable for anyone who relies on stamina and endurance. Similarly, Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) aids in breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and is vital for maintaining energy supply.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Supports over 200 chemical reactions in the body, facilitating the conversion of nutrients into energy.
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Essential for synthesizing coenzyme A, crucial for fatty acid metabolism.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Involved in amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis, aiding mental clarity.
To visualize how each B vitamin contributes to your energy levels, consider the following table:
| B Vitamin | Primary Role in Energy Metabolism |
|---|---|
| B1 (Thiamine) | Carbohydrate conversion |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | Fat, protein, and carb breakdown |
| B3 (Niacin) | Energy transformation in cells |
| B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Fatty acid metabolism |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Amino acid and neurotransmitter processing |








































