In recent years, the topic of gut health has emerged as a cornerstone of overall well-being, capturing the attention of health enthusiasts, medical professionals, and curious minds alike. Central to this conversation is the role of fermented foods, age-old culinary treasures that have nourished countless generations across diverse cultures. As we navigate the complexities of modern living, with its processed diets and fast-paced routines, understanding the profound impact of these foods on our digestive health becomes not just beneficial, but essential. This article delves into the symbiotic relationship between fermented foods and our gut microbiome, offering insights into how these nutrient-rich edibles can foster a balanced, thriving digestive system. Whether you’re new to the world of fermentation or seeking to deepen your knowledge, we aim to guide you with empathy and clarity, empowering you to make informed choices that nurture your body from the inside out.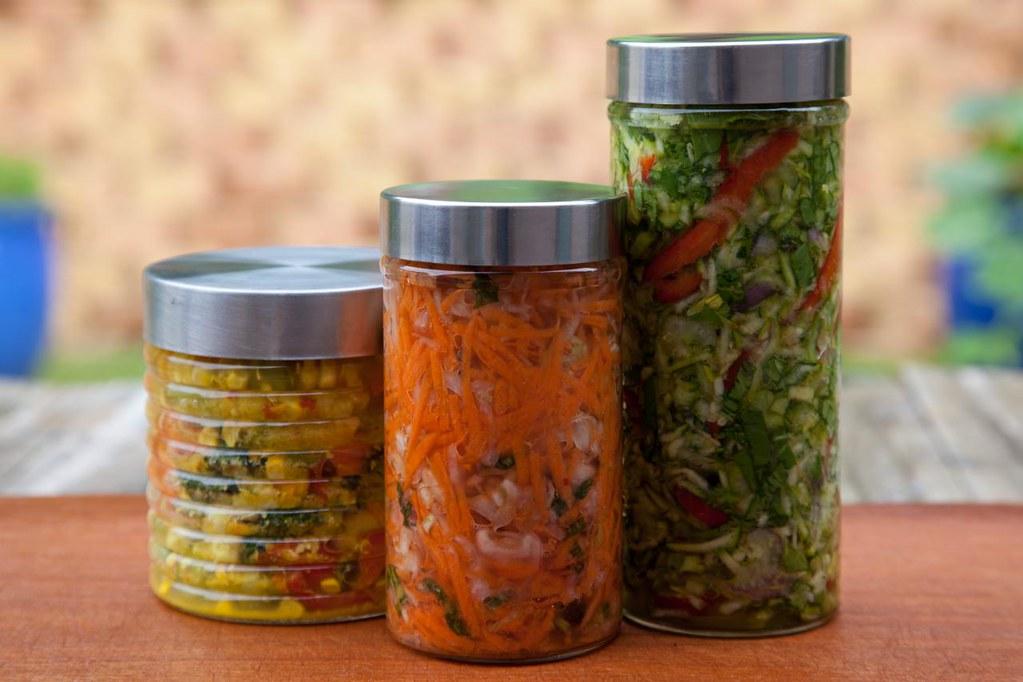
Understanding the Science Behind Fermented Foods and Gut Health
Fermented foods have been consumed for centuries, revered not only for their unique flavors but also for their profound impact on gut health. At the heart of this relationship is the process of fermentation itself, which transforms ordinary foods into potent sources of probiotics. These beneficial bacteria are vital for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: Fermentation breaks down complex nutrients, making them more accessible to the body.
- Production of Beneficial Enzymes: The fermentation process generates enzymes that aid in digestion.
- Support for Immune Health: A healthy gut microbiome can bolster the body’s immune defenses.
Let’s take a closer look at some common fermented foods and their specific benefits:
| Food | Primary Probiotic | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Yogurt | Lactobacillus | Improves digestion |
| Kefir | Multiple strains | Enhances gut diversity |
| Kimchi | Lactobacillus | Boosts immune health |
| Sauerkraut | Lactobacillus | Reduces inflammation |
Incorporating these foods into your diet can be a simple yet effective way to support gut health. By nurturing the microbiome, fermented foods help create an environment where beneficial bacteria can thrive, offering a natural, delicious pathway to enhanced well-being.

Exploring the Variety of Fermented Foods for a Balanced Diet
- Yogurt: A staple in many households, yogurt is a creamy delight that comes packed with probiotics. It’s not only a versatile breakfast option but also a gut-friendly snack that can be easily paired with fruits, nuts, or even savory dishes.
- Kimchi: This spicy Korean delicacy is made from fermented vegetables like cabbage and radishes. Rich in vitamins A, B, and C, kimchi is also loaded with healthy bacteria that aid in digestion.
- Kefir: Often compared to yogurt, kefir is a fermented milk drink that contains more strains of beneficial bacteria. It’s a great addition to smoothies or enjoyed on its own.
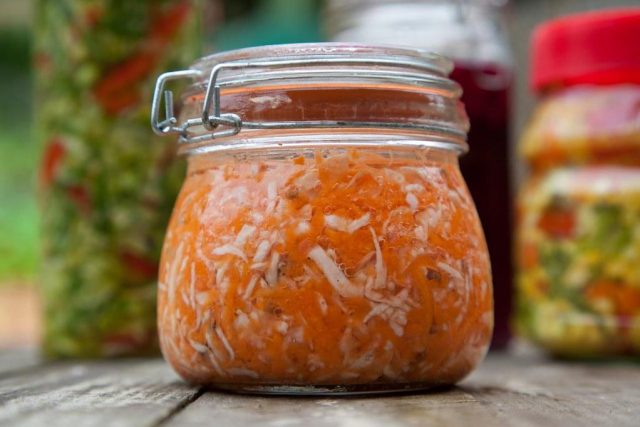
- Sauerkraut: A traditional German side dish made from fermented cabbage, sauerkraut is not only low in calories but also high in dietary fiber, aiding in digestion and promoting a healthy gut.
- Miso: This Japanese paste made from fermented soybeans adds umami flavor to soups, marinades, and sauces, while offering gut-friendly probiotics.
| Food | Main Benefit |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Probiotic-rich, supports digestion |
| Kimchi | Boosts immune system |
| Kefir | Improves gut flora diversity |
| Sauerkraut | High in fiber, aids in digestion |
| Miso | Enhances gut health with enzymes |
Incorporating these foods into your daily diet can be an exciting culinary adventure. By doing so, you not only enrich your meals with flavors but also nourish your body with beneficial bacteria that play a crucial role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. Remember, balance is key, and these diverse options allow for a fun exploration of tastes while keeping your digestive system in check.

Incorporating Fermented Foods into Your Daily Routine
Introducing fermented foods into your daily diet can be both enjoyable and rewarding. These probiotic-rich foods not only enhance the flavor of your meals but also support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome. To make this transition seamless, consider the following tips:
- Start small: Begin by incorporating small portions of fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, or yogurt into your meals. This allows your digestive system to adjust gradually.
- Mix and match: Combine different types of fermented foods to explore new flavors and textures. Try adding a spoonful of kimchi to your salad or a dollop of kefir to your smoothie.
- Experiment with recipes: Use fermented foods in various dishes. For example, add miso paste to soups or marinades for an umami boost.
| Fermented Food | Suggested Meal |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Breakfast parfait with berries and granola |
| Kimchi | Stir-fried rice or noodle bowl |
| Miso | Soup or salad dressing |
Remember, the key is consistency. Regularly consuming a variety of fermented foods can contribute to a healthier gut microbiome over time. Be patient and listen to your body, adjusting portions and types as needed. Embrace this journey to wellness with curiosity and enjoy the vibrant flavors these foods bring to your table.

Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions About Fermented Foods
When it comes to fermented foods, many people express concerns about their safety, taste, and benefits. It’s important to address these misconceptions to help individuals make informed dietary choices. Below are some common concerns and the truths behind them:
- Safety of Fermented Foods: A frequent worry is whether these foods are safe to consume. Fermented foods are generally safe when prepared properly. The fermentation process naturally preserves food and prevents the growth of harmful bacteria. However, it’s crucial to follow recommended preparation methods to ensure safety.
- Taste and Smell: Fermented foods often have strong flavors and odors that can be off-putting to newcomers. These characteristics are due to the natural fermentation process and can vary widely between different types of fermented foods. Trying a variety of products can help you find ones that suit your palate.
- Health Benefits: Some individuals are skeptical about the health claims surrounding fermented foods. While they are not a cure-all, research supports their role in promoting gut health. They introduce beneficial probiotics to the digestive system, aiding in digestion and potentially boosting immune function.
| Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| All fermented foods are high in alcohol. | Most fermented foods contain minimal alcohol levels, except for those specifically brewed as alcoholic beverages. |
| Fermented foods are too salty. | While some contain salt, many options are available with varying salt levels, such as yogurt and kefir. |